A sluggish VPN connection can be incredibly frustrating, hindering productivity and enjoyment. Whether you’re streaming movies, working remotely, or simply browsing the web, a slow VPN significantly impacts your online experience. This guide delves into ten practical troubleshooting tips to help you identify and resolve the root cause of your slow VPN, ensuring a seamless and high-speed connection.
From examining your network configuration and optimizing VPN settings to addressing external factors like interfering applications and outdated router firmware, we’ll explore a comprehensive range of solutions. Understanding the interplay between VPN protocols, server locations, and network conditions is crucial for achieving optimal performance. By following these steps, you can regain control over your online speed and enjoy a consistently fast and reliable VPN connection.
Identifying the Source of Slowdowns
A slow VPN connection can be frustrating, hindering productivity and online experiences. Pinpointing the exact cause requires a systematic approach, examining various factors that contribute to reduced speed. Understanding these factors is crucial for effective troubleshooting. This section details common causes and provides diagnostic methods to help you identify and resolve the issue.
Slow VPN speeds stem from a variety of sources, often interacting in complex ways. Network congestion on your end, limitations imposed by the VPN server itself, or even problems with your hardware can all significantly impact performance. Accurate diagnosis is key to finding the solution.
Common Causes of Slow VPN Connections
The following table Artikels common causes, their accompanying symptoms, and potential solutions. Identifying the symptoms will help guide your troubleshooting efforts.
| Cause | Symptoms | Potential Solutions | Further Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Network Congestion (Your Network) | Slow download/upload speeds across all applications, high latency (ping), intermittent connectivity drops. | Restart your modem and router; check for competing bandwidth-intensive applications; contact your internet service provider (ISP) to report potential network issues. | Consider upgrading your internet plan for increased bandwidth if congestion is consistently a problem. |
| VPN Server Overload | Slow speeds specifically when using the VPN, regardless of other applications; connection instability; high latency. | Try connecting to a different server; check the VPN provider’s status page for any reported outages or high load on specific servers. | Opt for a VPN provider with a larger network of servers and better infrastructure. |
| Faulty Hardware (Router, Modem, Network Card) | Slow speeds across all applications, including when the VPN is not active; intermittent connectivity; error messages related to network hardware. | Check physical connections; try replacing cables; update or replace your router or modem if necessary; test with a different network card (if applicable). | Consider hardware diagnostics tools to identify potential hardware failures. |
| VPN Software Issues | Slow speeds only when using the specific VPN software; errors or crashes within the VPN client; inability to connect or maintain a connection. | Reinstall the VPN software; update the VPN client to the latest version; check for conflicts with other software or firewall settings. | Ensure the VPN software is compatible with your operating system and other installed applications. |
Diagnosing Slow VPN Connections
Several methods can help isolate the cause of your slow VPN connection. Starting with simple checks and progressing to more advanced techniques is recommended.
- Check Your Internet Speed Without VPN: Run a speed test (e.g., Ookla Speedtest) without the VPN active. A slow result indicates a problem with your internet connection, not necessarily the VPN itself.
- Try a Different Server: Connecting to a different VPN server can immediately reveal if the problem lies with the server you were initially using (e.g., it’s overloaded).
- Test Different VPN Protocols: VPN protocols (like OpenVPN, WireGuard, IKEv2) have different performance characteristics. Experimenting with different protocols can sometimes resolve speed issues.
- Check for Network Interference: Wireless interference (from other devices, appliances) can impact VPN speeds. Try connecting via Ethernet cable or moving closer to your router.
- Examine VPN Client Settings: Ensure your VPN client isn’t configured to restrict bandwidth or prioritize specific applications. Check for any advanced settings that might be unintentionally limiting performance.
Geographical Location and Server Selection
Geographical distance significantly impacts VPN connection speed. Signals take time to travel, and longer distances mean increased latency and slower speeds. Optimizing server selection is key to maximizing performance.
Selecting a server closer to your physical location generally results in faster speeds. Many VPN providers allow you to filter servers by location, allowing you to choose one in your region or a nearby country. Experiment with different server locations to determine which offers the best performance for your needs. For instance, a user in London might experience faster speeds connecting to a UK-based server compared to one in Australia.
Optimizing VPN Settings and Configuration
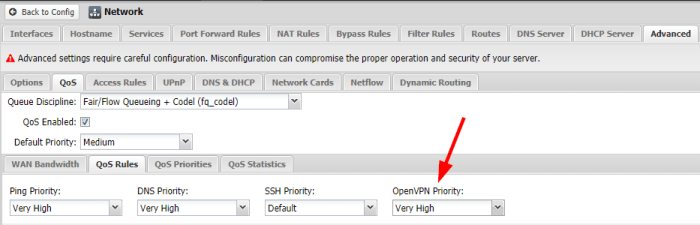
Optimizing your VPN settings can significantly impact connection speed. By carefully adjusting protocols, encryption levels, and other parameters, you can often resolve slowdowns and achieve a more efficient VPN experience. This section provides a structured approach to fine-tuning your VPN configuration for optimal performance.
Careful configuration of your VPN settings is crucial for maximizing speed and security. The following steps Artikel key areas to review and adjust.
Step-by-Step Guide to Optimizing VPN Settings
- Choose the Right VPN Protocol: Different protocols offer varying balances between speed and security. OpenVPN, WireGuard, and IKEv2 are popular choices, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Experiment to find the best protocol for your network and device.
- Adjust Encryption Level: Higher encryption levels offer stronger security but consume more processing power, potentially reducing speed. Consider lowering the encryption level if speed is a major concern, but be aware of the security trade-off.
- Optimize MTU Settings: The Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) defines the largest size of data packets that can be transmitted over a network. A poorly configured MTU can lead to packet loss and slowdowns. Experiment with slightly lower MTU values (e.g., 1400 or 1300) to find the optimal setting for your network.
- Select the Optimal Server Location: The physical distance between you and the VPN server significantly impacts latency and speed. Choose a server location that is geographically closer to you for faster connections.
- Avoid Overloaded Servers: If your chosen server is heavily congested, it will impact performance. Try connecting to a less crowded server within the same region.
- Check for DNS Leaks: DNS leaks can route your traffic outside your VPN tunnel, reducing speed and compromising your security. Use a DNS leak test to ensure your DNS requests are being routed through the VPN.
- Update your VPN Client: Outdated VPN clients may contain bugs or inefficiencies that negatively impact performance. Regularly update your client to the latest version.
- Restart your Device and Router: A simple restart can often resolve temporary network glitches that may be affecting your VPN connection.
- Disable Firewall Interference: Your firewall may be blocking VPN traffic. Temporarily disable your firewall to check if it is causing the slowdown. If so, configure your firewall to allow VPN traffic.
- Contact your VPN Provider: If you’ve tried all the above steps and still experience slowdowns, contact your VPN provider’s support team for assistance.
VPN Protocol Comparison: Speed and Security
The choice of VPN protocol significantly impacts both speed and security. Understanding the trade-offs is crucial for optimizing your connection.
| Protocol | Speed | Security |
|---|---|---|
| OpenVPN | Moderate to Slow (depending on encryption and configuration) | High; highly configurable and customizable |
| WireGuard | Fast | High; modern and efficient |
| IKEv2 | Fast | High; good for mobile devices |
Port Forwarding Configuration for VPN
Port forwarding allows you to forward specific ports from your router to your VPN client, which can improve performance, especially for applications that require consistent connections. However, improperly configured port forwarding can pose security risks. This should only be done if you understand the implications.
- Access your Router’s Configuration: Access your router’s settings through your web browser by typing its IP address into the address bar.
- Locate Port Forwarding Settings: The exact location of these settings varies depending on your router’s make and model. Look for options like “Port Forwarding,” “Virtual Servers,” or “NAT Forwarding.”
- Specify the Port and Protocol: Enter the port number you want to forward (e.g., 80 for HTTP, 443 for HTTPS) and select the protocol (TCP or UDP).
- Enter your VPN Client’s IP Address: Enter the internal IP address of your device running the VPN client.
- Save Changes: Save the changes to your router’s configuration. Restart your router to ensure the changes take effect.
Troubleshooting steps for port forwarding issues include checking your router’s logs for errors, ensuring the port isn’t already in use, and verifying your VPN client’s IP address. Incorrectly configured port forwarding can create security vulnerabilities, so proceed with caution.
Addressing External Factors Affecting Speed

A slow VPN connection isn’t always due to the VPN itself. External factors competing for your network’s bandwidth can significantly impact performance. Understanding these factors and taking steps to mitigate their influence is crucial for optimizing your VPN speed. This section will explore potential sources of interference and provide practical solutions.
Understanding that your internet connection is a shared resource, it’s important to identify and address any applications or devices that might be hogging bandwidth. This can lead to noticeable slowdowns, especially when using a VPN which already adds some overhead.
Network Device and Application Interference
Many devices and applications can compete for bandwidth, impacting your VPN speed. Identifying these culprits is the first step towards resolution.
- Other Internet Users: If multiple devices are connected to your network simultaneously, streaming videos, downloading large files, or engaging in online gaming, your VPN connection will likely suffer. The more devices competing for bandwidth, the slower your VPN connection will be.
- Bandwidth-Intensive Applications: Applications like torrent clients, cloud storage synchronization software, and online gaming platforms consume considerable bandwidth. Running these concurrently with your VPN can drastically reduce VPN speed.
- Background Processes: Many applications run background processes that consume bandwidth without your explicit knowledge. These can include software updates, system maintenance tasks, and even certain browser extensions.
- Network Hardware Limitations: An older or overloaded router may struggle to handle the additional traffic generated by a VPN, leading to noticeable slowdowns. Similarly, a saturated internet connection from your ISP can limit the overall speed regardless of the VPN.
Minimizing External Interference
A systematic approach to minimizing external interference is vital. The following checklist Artikels steps to identify and address potential bandwidth hogs.
- Temporarily Disable Non-Essential Applications: Close all unnecessary applications running in the background. This includes web browsers with multiple tabs open, streaming services, and download managers.
- Pause Downloads and Uploads: Halt any ongoing downloads or uploads, particularly large files, to free up bandwidth for your VPN connection.
- Temporarily Disable Firewalls and Antivirus Software: While not recommended for extended periods, temporarily disabling your firewall and antivirus software can help determine if they are contributing to the slowdown. Remember to re-enable them afterward.
- Prioritize VPN Traffic: Some routers allow you to prioritize specific applications’ network traffic. If your router supports Quality of Service (QoS) settings, prioritize your VPN connection to ensure it receives sufficient bandwidth.
- Restrict Bandwidth Usage on Other Devices: If you have multiple devices connected to your network, consider temporarily limiting bandwidth usage on less critical devices.
Router Settings and Firmware Updates
Outdated or improperly configured router firmware can significantly impact VPN performance. Regular firmware updates often include performance enhancements and bug fixes that can improve your VPN speed.
- Check for Firmware Updates: Access your router’s administration interface (usually via a web browser) and look for a firmware update section. Follow the instructions provided to update to the latest version.
- Review Router Settings: Examine your router’s settings for any limitations on bandwidth or traffic prioritization that might be affecting your VPN connection. Consult your router’s manual for specific instructions on adjusting these settings.
- Restart Your Router: A simple restart can often resolve minor network glitches that might be impacting your VPN speed. Unplug the router from the power outlet, wait 30 seconds, and then plug it back in.
Summary

Successfully troubleshooting a slow VPN connection often requires a systematic approach, combining technical understanding with practical problem-solving skills. By systematically checking your network infrastructure, optimizing your VPN settings, and addressing external factors, you can significantly improve your connection speed. Remember that patience and persistence are key – diagnosing the precise cause might involve several steps, but the reward of a fast and reliable VPN connection is well worth the effort. This guide has provided a solid foundation for resolving common issues; however, persistent problems may require consulting your VPN provider’s support documentation or contacting their technical support team.