File transfers are the backbone of modern digital life, yet they’re surprisingly prone to issues. From agonizingly slow speeds to frustrating interruptions and dreaded data corruption, these problems can halt productivity and cause significant headaches. This guide delves into seven common file transfer challenges, providing practical solutions and preventative strategies to ensure your data travels smoothly and safely.
Understanding the underlying causes of these problems – whether it’s network congestion, hardware limitations, or file corruption – is crucial for effective troubleshooting. We’ll explore various file transfer protocols, diagnostic tools, and best practices to equip you with the knowledge to navigate these common obstacles and maintain a seamless workflow.
Slow Transfer Speeds
Slow file transfer speeds can be incredibly frustrating, especially when dealing with large files or time-sensitive projects. Several factors can contribute to this issue, ranging from simple network congestion to more complex hardware problems. Understanding these causes and implementing appropriate solutions can significantly improve your file transfer efficiency.
Causes of Slow Transfer Speeds
Network congestion, insufficient bandwidth, and hardware limitations are common culprits behind slow transfer speeds. Network congestion occurs when too many devices are vying for the same bandwidth, leading to bottlenecks and slower speeds. Insufficient bandwidth, meaning your internet plan doesn’t provide enough speed for your needs, directly limits transfer rates. Hardware limitations, such as an outdated router or a slow hard drive, can also significantly impact transfer performance. Furthermore, the file transfer protocol used can also influence speed; some are inherently faster than others. Finally, background processes consuming bandwidth can also contribute to slower transfers.
Solutions for Improving Transfer Speeds
Several strategies can be employed to address slow transfer speeds. Upgrading your network hardware, such as your router and modem, can dramatically improve performance, especially if your current equipment is outdated or struggling to handle the network load. Optimizing network settings, such as adjusting Quality of Service (QoS) settings to prioritize file transfers, can also yield improvements. Reducing network congestion by limiting the number of devices actively using the network during transfers can help. Finally, ensuring your hard drives and other storage devices are functioning optimally will contribute to faster transfer speeds.
File Compression Techniques
Compressing files before transferring them can significantly reduce transfer times, especially for large files. Common compression formats like ZIP and 7z can drastically reduce file sizes, resulting in faster transfers. The level of compression can be adjusted; higher compression levels generally result in smaller files but take longer to compress and decompress. Choosing the appropriate compression level involves balancing file size reduction with the time spent on compression and decompression.
Troubleshooting Slow Transfer Speeds
Troubleshooting slow transfer speeds often involves using network diagnostic tools. These tools can identify bottlenecks and pinpoint the source of the problem. For example, using tools like ping and traceroute can help determine network latency and identify potential issues along the data path. Network monitoring software can provide a comprehensive overview of network traffic, highlighting potential congestion points. Similarly, checking the resource monitor on your computer can reveal if the CPU, memory, or hard drive is becoming a bottleneck during the transfer.
Comparison of File Transfer Protocols
Different file transfer protocols offer varying levels of speed and security. The choice of protocol can significantly impact transfer performance.
| Protocol | Speed | Security | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| FTP | Moderate | Low (unencrypted) | Simple to use, but vulnerable to attacks without SSL/TLS |
| SFTP | Moderate to High | High (encrypted) | Secure version of FTP, using SSH for encryption |
| SCP | Moderate to High | High (encrypted) | Secure copy protocol, utilizes SSH for encryption and is often faster than SFTP |
Failed Transfers and Interruptions
File transfers, while seemingly straightforward, can be prone to failure or interruption. This often leads to frustration and potential data loss. Understanding the common causes and implementing preventative measures is crucial for a smooth and reliable file transfer experience. This section will explore the reasons behind failed transfers, strategies for prevention, and methods for recovery.
Failed file transfers and interruptions can stem from various sources. Corrupted files, insufficient storage space on the receiving end, and network connectivity problems are among the most frequent culprits. A weak or unstable internet connection, for instance, can easily disrupt a large file transfer mid-process. Similarly, a full hard drive or insufficient disk space on the destination device will abruptly halt the transfer. Furthermore, issues with the file itself, such as corruption during creation or transmission, can lead to failure.
Causes of Failed File Transfers
Several factors contribute to the failure of file transfers. These include, but are not limited to, file corruption due to transmission errors or disk errors, insufficient storage space on the receiving device, network connectivity issues such as dropped packets or temporary outages, and problems with the transfer protocol itself. For example, using an outdated or incompatible protocol can lead to incompatibility issues and transfer failures. In cases where a file is corrupted, it might be unreadable by the receiving system, leading to a failed transfer.
Preventing File Transfer Interruptions
Proactive measures can significantly reduce the incidence of interrupted transfers. Utilizing robust and reliable transfer protocols, such as SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol) or FTPS (File Transfer Protocol Secure), offers enhanced security and reliability compared to less secure options like FTP. These protocols incorporate error-checking mechanisms and data integrity checks, minimizing the risk of data corruption during transfer. Furthermore, ensuring a stable and high-bandwidth internet connection is paramount. This reduces the likelihood of connection drops and improves overall transfer speed and reliability. Regularly checking and clearing storage space on the receiving device prevents transfers from being halted due to insufficient space.
Resuming Interrupted Transfers
Many modern file transfer applications and cloud services offer resumable upload and download features. This functionality allows you to pick up where you left off after an interruption, preventing the need to restart the entire transfer. For example, services like Dropbox, Google Drive, and OneDrive incorporate this feature, automatically resuming downloads or uploads following a network interruption or other unforeseen event. This significantly reduces the time and effort required to complete large file transfers.
Recovering from Failed File Transfers
If a file transfer fails completely, data recovery techniques might be necessary. The first step is to check the source and destination devices for any partial or corrupted files. If a partial file exists, it may be possible to resume the transfer using the resumable feature, if available. If the file is completely lost, specialized data recovery software may be needed. These tools can scan storage media and attempt to recover lost or corrupted files, but success isn’t guaranteed. It’s crucial to act quickly as overwriting the affected storage space can permanently erase the lost data.
Best Practices for Successful File Transfers
Implementing best practices can drastically improve the reliability of your file transfers. This includes using secure and reliable protocols, ensuring sufficient storage space on the receiving device, maintaining a stable internet connection, verifying file integrity before and after transfer, and utilizing resumable transfer features whenever possible. Regularly backing up important data provides an additional layer of protection against data loss due to failed transfers. By adopting these practices, you can minimize interruptions and ensure successful completion of your file transfers.
File Corruption and Data Loss
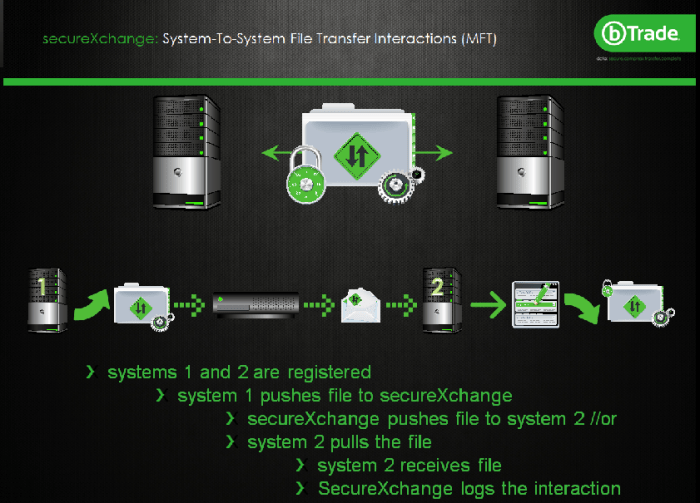
File corruption during transfer can lead to significant data loss, rendering files unusable or incomplete. Understanding the causes, prevention, and recovery methods is crucial for maintaining data integrity. This section explores various techniques to detect, prevent, and recover from file corruption, ensuring the reliable transfer of your important data.
Detecting File Corruption
Several methods exist for identifying corrupted files. Checksum verification involves generating a unique digital fingerprint of a file before and after transfer. Any discrepancy indicates corruption. Data integrity checks, often built into file systems or applications, compare file attributes against expected values to detect inconsistencies. Checksum methods, like MD5 or SHA-256, provide a more robust check than simple size comparisons, as they examine the file’s content directly. While checksums offer a strong method for detecting corruption, they don’t always pinpoint the location or extent of the damage. Data integrity checks, on the other hand, can offer more context but might not detect subtle forms of corruption that checksums would catch.
Preventing File Corruption During Transfer
Proactive measures significantly reduce the risk of file corruption. Error-correcting codes (ECC) are algorithms that add redundancy to data, allowing the reconstruction of lost or corrupted information. ECC is commonly used in storage media and network protocols. Implementing robust backup strategies is equally important. Regularly backing up files to a separate location, such as an external hard drive or cloud storage, allows recovery in case of data loss. The use of multiple backups, in different locations, minimizes the risk of catastrophic loss from events such as fire or theft. Employing a version control system can further safeguard against accidental modifications or corruption.
Recovering Data from Corrupted Files
Data recovery software employs sophisticated algorithms to scan corrupted files and attempt to reconstruct usable data. The success rate varies depending on the severity of the corruption and the file type. Professional data recovery services offer advanced tools and expertise for more complex cases, often recovering data from severely damaged storage media. While data recovery software is readily available, professional services should be considered for critical data or when simpler methods fail. It’s important to remember that attempting recovery yourself may unintentionally worsen the corruption, making professional help a worthwhile investment in such situations.
Implementing Robust File Transfer Procedures
Minimizing data loss requires a multi-faceted approach. Using reliable transfer protocols, such as FTP with secure encryption (FTPS or SFTP), protects data during transit. Verifying file integrity after transfer, using checksum verification, confirms the data arrived undamaged. Implementing data transfer logging provides an audit trail to help identify and troubleshoot potential issues. Regularly testing the transfer process using sample files helps identify and address vulnerabilities before they impact critical data. Scheduled backups and version control, as previously discussed, further strengthen the resilience of the data transfer process.
Impact of File Formats on Data Integrity
Different file formats have varying levels of resilience to corruption. Binary formats, like executable files (.exe), are more susceptible to corruption than text-based formats (.txt), as even a single bit error can render them unusable. Compressed files (.zip, .rar) can also be vulnerable; corruption in the compressed data can lead to complete data loss. Choosing appropriate file formats based on the sensitivity of the data and the transfer environment is crucial. Using formats with built-in error detection and correction mechanisms, where available, can help to mitigate the risk of data loss. For example, choosing a format with checksums or parity bits embedded can improve the reliability of transfer.
Conclusion

Successfully navigating the complexities of file transfers requires a proactive approach combining preventative measures and effective troubleshooting techniques. By understanding the common pitfalls and implementing the strategies Artikeld in this guide, you can significantly reduce the risk of encountering problems and ensure the reliable and efficient transfer of your valuable data. Remember, a well-planned and executed file transfer process is essential for maintaining productivity and data integrity in today’s digital world.